EthernetKRL
Quickstart
Make sure that the option EthernetKRL is installed on your controller. Next log into the frontend at https://www.vathos.vision, navigate to the devices page, and make sure the KUKA KRL Connector app is installed on the edge device designated for communication with this robot:

Navigate to our Github examples page and download the release whose version number matches the one of the app you just installed:
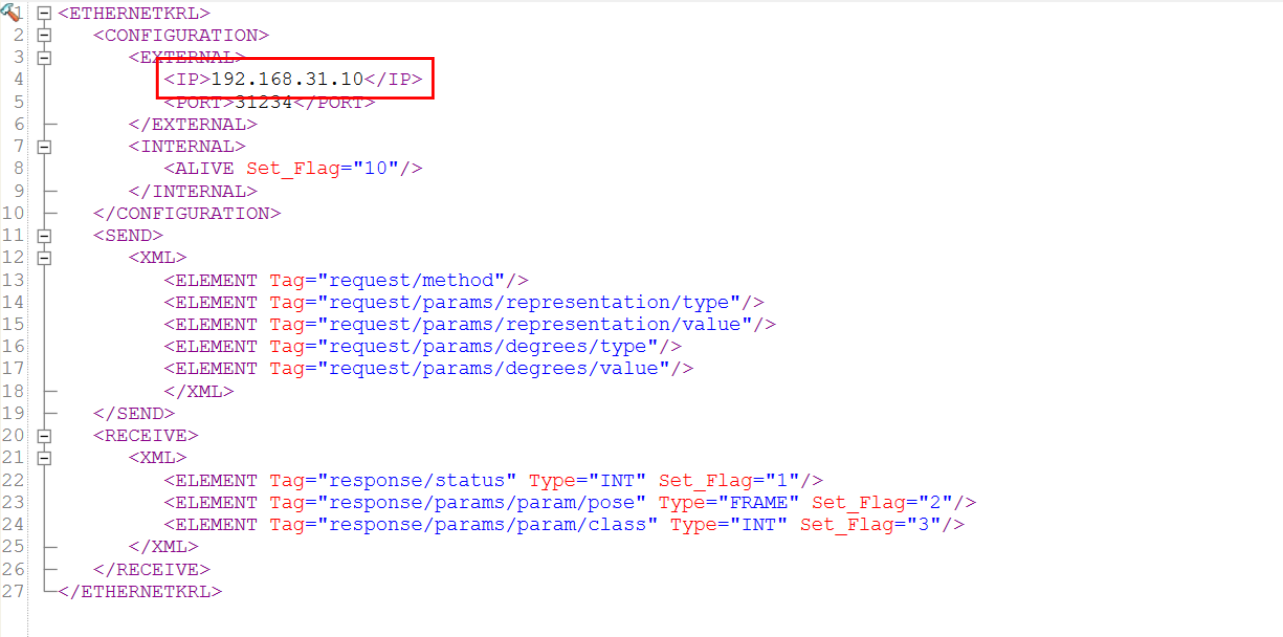
Unpack the downloaded zip file. The folder /config contained therein holds a set of XML configuration files, each defining an API function that can be called in KRL. In each file, adjust the value of the server IP to match the IP of the edge device:
The edge device will act as server, the KRC controller will act as client. Copy all configuration files to the folder /Config/User/Common/EthernetKRL on the controller using either a USB stick or WorkVisual:
Execute a cold reboot of the controller making sure that the flag for reading in updates of the configuration is checked. Finally copy the folder /vathos from the zip file to a location somewhere below the path /KRC/R1/Program on the controller. Each of the files in that directory implements a KRL function wrapping functions from our API in a call via EthernetKRL.
Intentionally, the names and arguments of the KRL functions in general match those of our API functions. Note, however, the KRL functions reside in the global scope, and thus, there may be clashes with other program symbols. In that case, the violating functions can be renamed, e.g., by pre-fixing them with vathos so that trigger becomes vathos_trigger.
Here is a short example of a pick & place program using our service for detecting rod-like objects:
DEF pick_and_place()
DECL pick_frame = $NULLFRAME
DECL api_success = FALSE
DECL INT product_index = -1
DECL INT class_index = -1
; camera is mounted on arm with TCP estimated via hand-eye calibration
; BASE_DATA[1] contains a base over the region of interest (e.g., a pallet)
; with z axis pointing towards it
$TOOL = TOOL_DATA[1]
$BASE = BASE_DATA[1]
; move the camera so that it coincides with the base
PTP { X 0, Y 0, Z 0, A 0, B 0, C 0}
; trigger the image capture and evaluation
; this blocks until capture is complete
api_success = trigger('rods', TRUE)
IF NOT api_success THEN
HALT
ENDIF
; now use gripper with tool no. 2
$TOOL = TOOL_DATA[2]
LOOP
; pop a pose/classification from the list of computed poses
; wait at most 20 s for the (first) detection
api_success = get_pose(pick_frame, product_index, class_index, 'rods', 20)
IF NOT api_success THEN
EXIT
ENDIF
; the pose is 100 mm over the final pick pose
; the value of the preposition distance can be configure on the edge device
PTP pick_frame
; move down in z-direction of the tool to make contact
LIN_REL { Z 100 } #TOOL
; wait and activate the gripper
WAIT SEC 0.1
OUT[1] = TRUE
; move out
LIN_REL { Z -100 } #TOOL
ENDLOOP
END
This short program contains two calls to the Vathos API:
-
trigger triggers the camera to capture a new image. Since multiple different apps/workflows for evaluation may be run on the same edge device (even in the same process), the desired workflow must be indicated by the value of the first argument (here
"rods"). The second argument tells the interpreter to block the execution of the KRL program until image acquisition (not evaluation!) has completed and it is safe to keep moving the robot without intruding the field of view. Note that immediately after the acquisition is finished, the analysis of the image begins and keeps detecting objects while the robot program continues until a predefined constant maximum processing time is exceeded. -
New poses obtained by the evaluation algorithm are put in a (priority) queue on the edge device and can be retrieved one by one by invoking get_pose. Note that some workflows include information about the type/state of object which are written into the variables passed to the function as the second and third argument. The fourth argument indicates the workflow to retrieve poses from (similar to the first argument of the trigger function). The last argument defines the maximum time in seconds
get_poseshould wait for new detections to be put on the queue by the evaluation algorithm.